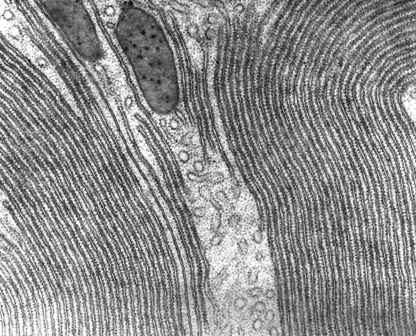
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), an extensive network
of tubes that manufacture, process, and transport
materials within nucleated cells. The ER consists of a
continuous membrane in the form of branching tubules
and flattened sacs that extend throughout the
cytoplasm (the cell's contents outside of the nucleus)
and connect to the double membrane that surrounds
the nucleus. There are two types of ER: rough and
smooth.
The outer surface of rough ER is covered with tiny
structures called ribosomes, where protein synthesis
occurs. Proteins are created as long polypeptide
chains, some of which require modification. These
proteins are transported into the rough ER, where
enzymes fold and link them into the three dimensional
shape that completes their structure. The rough ER
also transports proteins either to regions of the cell
where they are needed or to the Golgi apparatus, from
which they may be exported from the cell. Rough ER is
particularly dense in cells that manufacture proteins for
export. White blood cells, for example, which produce
and secrete antibodies, contain abundant rough ER.
Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and so has a smooth
appearance. It is involved in the synthesis of most of
the lipids that make up the cell membrane, as well as
membranes surrounding other cell structures like
mitochondria. It also manufactures carbohydrates,
stores carbohydrates and lipids, and detoxifies alcohol
and drugs such as morphine and phenobarbitol. Cells
that specialize in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism,
such as brain and muscle cells, or those that carry out
detoxification, such as liver cells , tend to have more
smooth ER.
Smooth ER also is involved in the uptake and release of
calcium to mediate some types of cellular activity. In
skeletal muscle cells, for example, the release of
calcium from the smooth ER triggers muscle
contraction.
Contributed By: John B. Ferguson, Sc.B., M.Phil., Ph.D.
Professor of Biology, Division of Natural Sciences and
Mathematics, Bard College. Director, Distinguished
Scientist Lecture Series, Bard Center.
Biology, © Microsoft
This image is an example of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. Smooth ER has none of the small black dots tha